대기복사/대기물리 연구실
교수
이윤곤 (기1303호)
학생연구실
기 1300호
연구분야
- 황사와 기후변동성의 관련성 연구
![동아시아 주요 황사 발원지 ( R1: 타클리마칸 사막, R2: 고비사막, R3:황토 고원) / 1998년 4월 21~24일 동안 TOMS AI로 관측한 동아시아 황사의 수송 공간분포 [Koo et al. 2016]](/_res/template_ne/img/pic/study01.jpg)
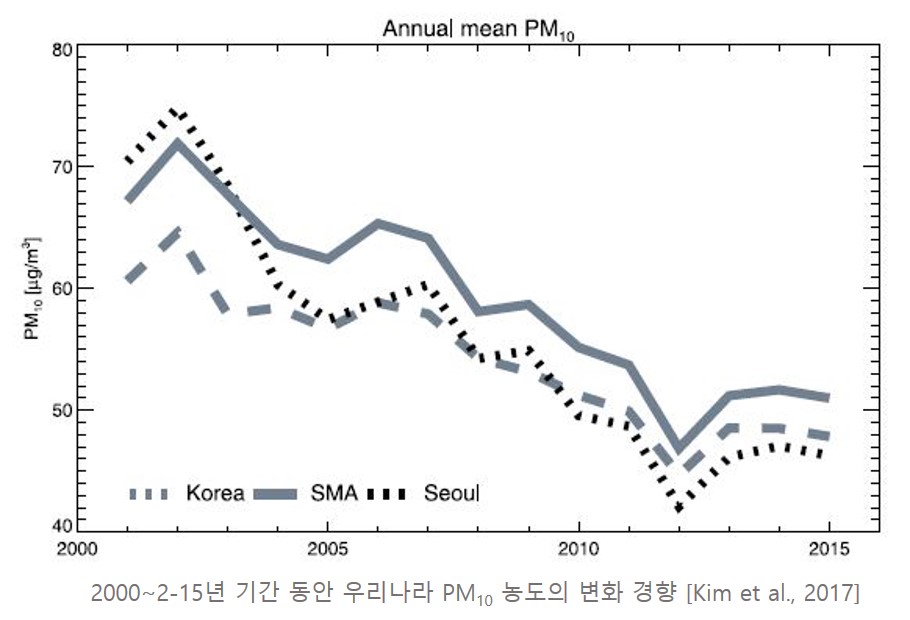
동북아시아 지역은 아시아 대륙의 대표적인 황사 발원지인 타클리마칸 사막, 고비 사막, 황토 고원에서 발생한 황사에 직접적인 영향을 받는 지역이다. 발원지에서 발생한 황사는 편서풍을 타고 중국 동부, 한반도, 일본 및 태평양을 거쳐 먼 아메리카 대륙으로까지 수송되기도 한다 (Zhang et al., 1997; Husar et al., 2001; Sun et al., 2001; Liu et al., 2004; Laurent et al., 2006; Uno et al., 2009). 아시아 사막에서 발원한 황사는 이동시에 중국의 주요 공업지대를 거쳐 대기 중 유해물질과 함께 이동되기 때문에 유해성이 증가하여 황사 수용지에 심각한 영향을 미치게 된다. 2000년 이후부터 한반도 지역에서의 황사 관측은 점차 감소하는 경향을 보였으나 최근 들어 다시 약간 증가하는 경향을 보이고 있다 (Kim et al., 2017).
대기복사/대기물리 연구실에서는 다양한 위성 및 지상 기반 관측 자료를 이용하여 동북아시아 황사의 발생 및 이동의 시공간적 변동성을 파악하고 특히 황사의 발생 및 수송에 영향을 미치는 기상학적 패턴이나 태평양 지역의 기후 변동 인자들과의 상관성 분석을 심도 있게 진행하고 있다.
- 위성 자료를 이용한 지상 미세먼지 정보 산출
"우리나라는 봄철 황사 발원지로부터 유입된 자연적 에어로졸과 중국 및 국내의 공업지역에서 방출된 인위적 에어로졸의 발생이 세계적으로 높게 나타나는 지역 중 하나이다 (Ohara et al., 2007; Yuan et al., 2008). 에어로졸은 입자 크기에 따라서 직경이 50 μm이하인 총 먼지(Total Suspended Particles, TSP)와 입자크기가 작은 미세먼지(Particulate Matter; PM)로 구분된다. 이 중 미세먼지는 다시 입자의 직경에 따라서 PM10(10 μm이하)과 PM2.5(2.5 μm이하)로 구분된다. 자연적 및 인위적으로 발생한 대기 중 PM10 및 PM2.5는 시정 악화뿐만 아니라 인체의 호흡기 및 심혈기관에 치명적인 영향을 주는 것으로 알려져 있다(WHO, 2005; IPCC, 2013). 자연적 및 인위적으로 발생한 대기 중 미세먼지는 시정의 악화뿐만 아니라 인체의 호흡 및 심혈관계에 치명적인 영향을 끼치고 전 지구적 기후변화에도 영향을 주는 요인으로 알려져 있다 (WHO, 2005; IPCC 2013). "
![2017년 1월 18일 서울 하늘 [한국일보]](/_res/template_ne/img/pic/study04.jpg)
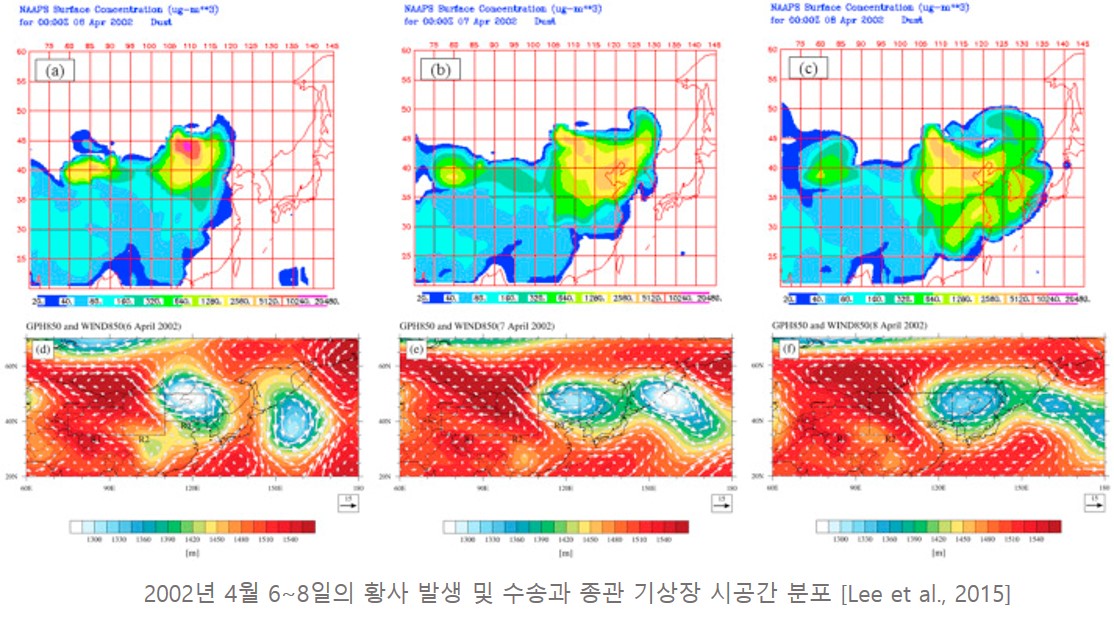
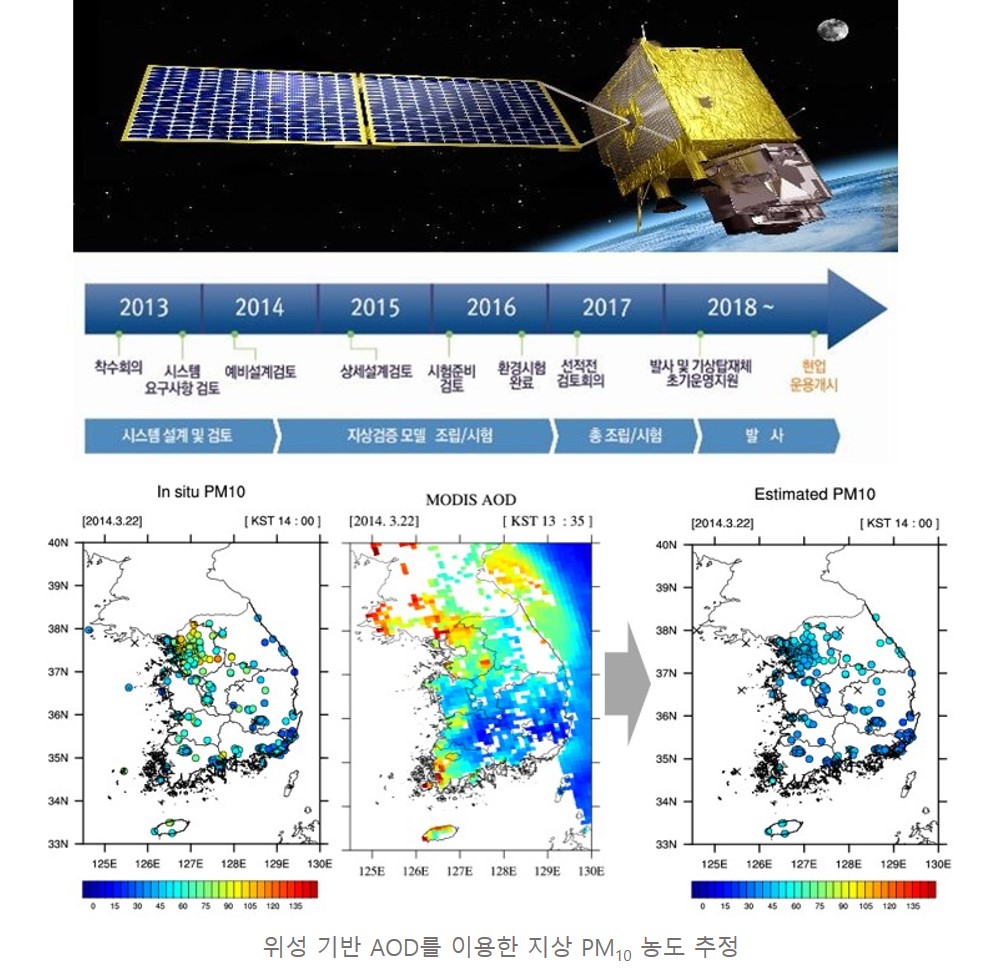
"대기복사/대기물리 연구실에서도 차세대 정지궤도 위성 (GK-2A) 기후/환경 활용 알고리즘 개발 연구의 일환으로서 극궤도 및 정지궤도 위성 기반의 AOD와 기상 재분석장 자료를 활용하여 지상 PM10 및 PM2.5 농도를 산출하는 연구를 활발히 진행 중이다. 위성 기반 관측의 AOD은 에어로졸에 의한 지상으로부터의 연직 광학 두께 정보이기 때문에 AOD 하나만으로는 정확한 지상 미세먼지 농도를 산출하는데 어려움이 있다. 따라서 행성 경계층 고도, 상대습도 (흡습성장 계수), 지표 풍속, 지표 기압 등의 기상인자를 함께 고려한 다중회귀모델을 이용해 보다 정확한 지상 미세먼지 농도 산출 모델을 개발 중에 있다."
- 태양 복사 자료를 이용한 대기혼탁도 연구 및 청천지수를 이용한 지표 자외선 산출 연구
"자외선, 가시광선, 근적외선 등의 태양복사는 지구 기후시스템과 생테계를 유지시키는 주된 에너지원이다. 전천일사 (Global solar radiation)은 지표에 도달하는 태양 에너지의 전체 복사량을 의미하며, 이는 지표 위의 대기 상태에 따라 시공간적으로 변화한다. 이러한 변화는 대기 중의 구름, 수증기, 에어로졸, 그리고 다른 기체들에 의한 복사량의 흡수와 산란과정으로 기인하나, 이 복잡한 과정들의 비선형적 상호작용으로 인해 변화 정도를 예측하는 것이 어렵다 (Che et al., 2005; Okogbue et al., 2009; Bano et al., 2013). 대기에서의 태양 복사 소산 정도를 정량화하기 위해 입사하는 태양복사에 영향을 미치는 대기 구성성분들이 결합된 기여도 분석이 필요하다. 이러한 소산과정들은 매우 복잡하지만 대기 외상한 태양복사량에 대한 지표 전천일사량의 비율인 청천지수를 정의하여 (Liu and Jordan, 1960; Iqbal, 1983; Ideriah and Suleman, 1989; Elhadidy et al., 1990; Udo, 2000) 태양복사의 투과도를 결정하는 변수이자 일반적인 지표로 사용되고 있다."
![한반도 지역 청천지수의 시공간적 분포 [Jung et al 2016]](/_res/template_ne/img/pic/study06.jpg)
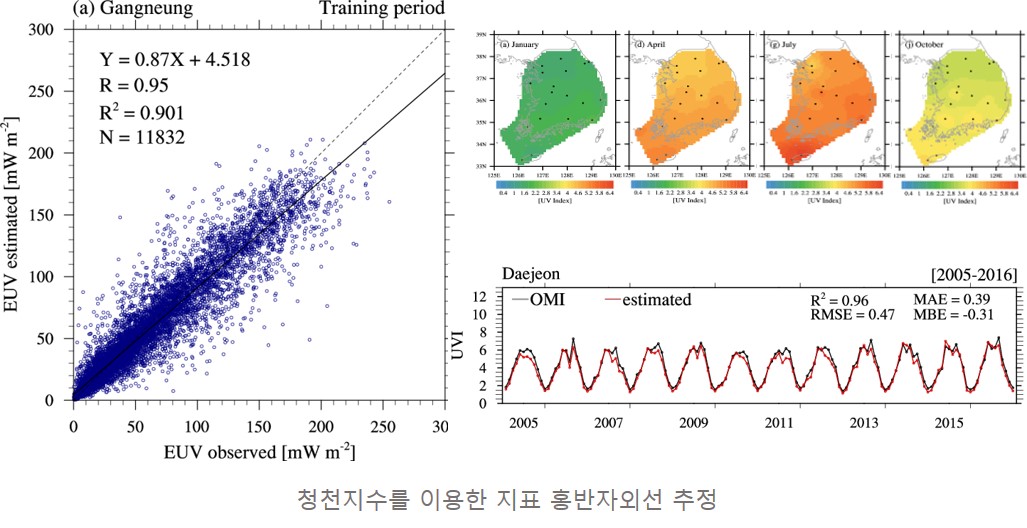
"대기복사/대기물리 연구실에서는 태양복사의 청천지수를 이용하여 한반도 지표 전천일사 및 자외선의 청천지수의 지역적인 특징과 이에 미치는 대기 인자들의 영향에 대해 분석하고, 전천일사와 자외선의 대기 투과도에서 나타나는 기상 인자들의 영향을 비교 분석 하는 연구는 진행하고 있다. 또한 지표 자외선 관측소가 부족한 한반도 지역에 대해 전천일사와 자외선의 대기 투과도 비교 분석 결과를 바탕으로 하여 청천지수 및 위성 오존 자료를 이용해 지표 도달 홍반자외선 복사량을 추정하고자 하는 실용적인 연구 또한 이루어지고 있다."
- 지표 자외선 복사량 자료를 이용한 공중보건 정보 산출
![자외선 [중앙일보]](/_res/template_ne/img/pic/study08.jpg)
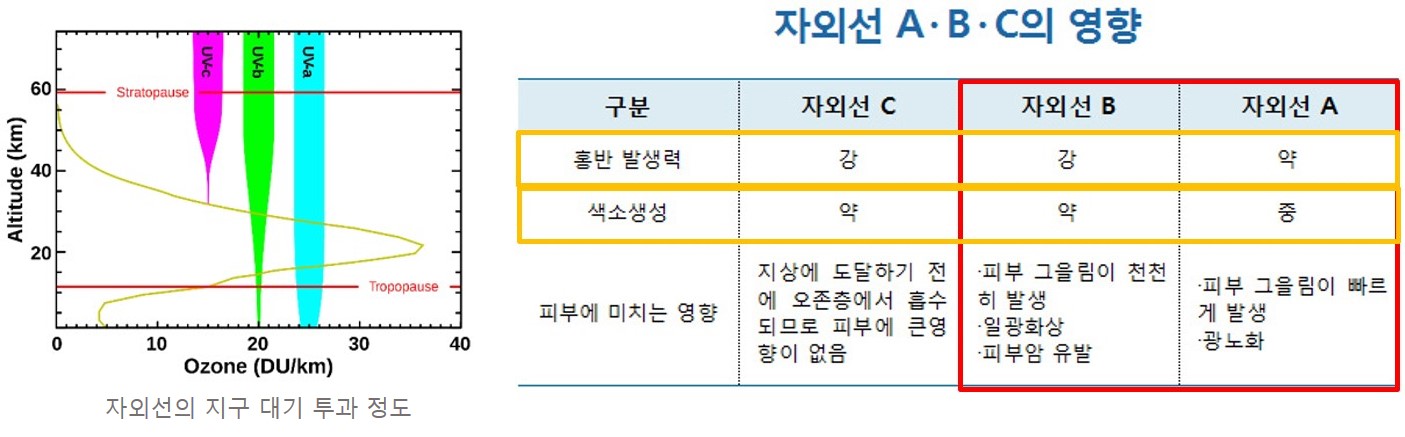
지표에 도달하는 자외선 복사 (100~400nm)의 유해성에 대한 정보는 세계보건기구 (World Helth Organization, WHO)나 세계기상기수 (World Meteorological Organization, WMO)에 의해 널리 보급되었으며, 우리나라를 포함한 세계 각국에서는 국민들을 대상으로 자외선 정보를 제공하고있다. 자외선은 파장에 따라 자외선C (100~280nm), 자외선B (280~320nm), 자외선A (320~400nm)로 구분되며 이 중 지표에 도달하는 자외선B와 자외선A 복사에 일정 시간 노출되면 홍반 (erythema) 발생, 피부암 (e.g. de Gruijl, 1999; Armstrong and Kricker, 2001), 백내장 (e.g. Taylor et al., 1988; Ayalaet al., 2000) 등의 발생하는 위험성이 높아지게 된다.
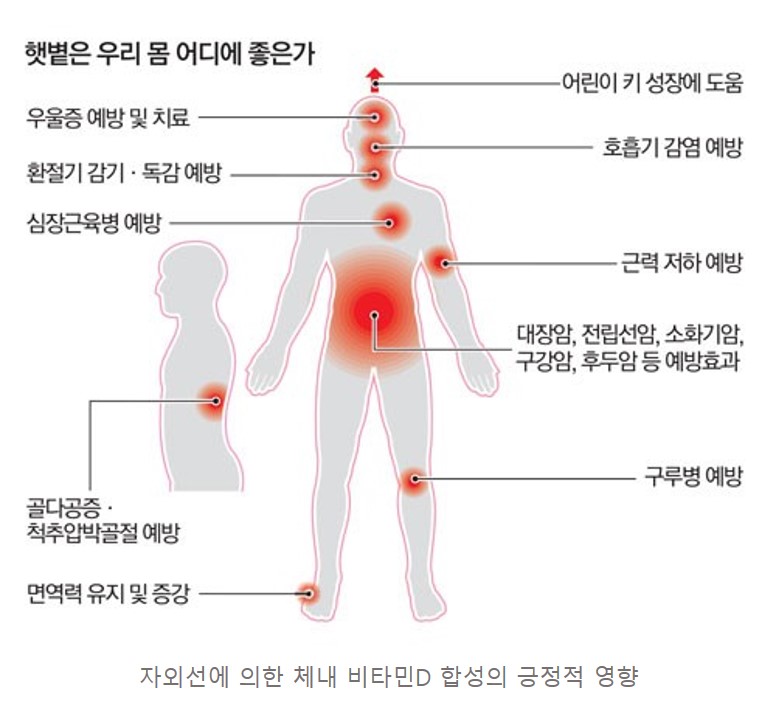
반면 자외선은 체내에서 합성이 불가능한 비타민D를 합성시키는 긍정적인 영향도 있으며, 자외선 노출 부족으로 인해 발생하는 비타민D 결핍은 가벼운 생활 건강 악화뿐만 아니라 골연화증 및 골다공증과 같은 근·골격계 질환, 심혈관 질환, 자가 면역 질환, 감염성 질환, 일부 암, 당뇨병 등의 발생 위험을 증가시키는 것으로 알려져 있다 (e.g., Lucas et al., 2006; Holick, 2007; WHO, 2008; Pludowski et al., 2013). 이러한 자외선의 부정적 및 긍정적인 영향을 고려하여 우리나라 국민에게 맞는 적정 자외선 노출시간 정보의 산출이 필요하며, 대기복사/대기물리 연구실에서는 이를 위해 장기간 동안의 지표 자외선 복사량 관측 자료를 이용하여 우리나라 국민에게 적적한 자외선 노출에 대한 지침을 제공을 목표로 연구를 진행 중이다 (관련 기사 : [중앙일보] 봄철 피부의 적 자외선A... 노화 막으려면 이것부터)
Publications
2020
- Kim, M., Kim, S. H.*, Kim, W., Lee, Y. G., Kim, J., and Kafatos, M. C.: Assessment of aerosol optical depth in polluted and background condition using AERONET and VIIRS dataset, Atmospheric Environment, accepted.
- Lee, J., Koo, J.-H., Kim, S.-M., Lee, T., and Lee, Y. G.*: Comparison of aerosol properties in the Korean Peninsula between AERONET version 2 and 3 data set, Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/ s13143-020-00221-2
- Koo, J.-H., Lee, J., Kim, J., Eck, T. F., Giles, D. M., Holben, B. N., Park, S. S., Choi, M., Kim, N., Yoon, J., and Lee, Y. G.*: Investigation of the relationship between the fine mode fraction and Angstrom exponent: Cases in Korea, Atmospheric Research, 248, 2020; doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105217
- Kim, C. K., Kim, H.-G., Kang, Y.-H., Yun, C.-Y., and Lee, Y. G.: Intercomparison of satellite-derived solar irradiance from the GEO-KOMSAT-2A and HIMAWARI-8/9 satellites by the evaluation with ground observations, Remote Sensing, 12, 2149, 2020; doi:10.3390/rs12132149
- Lee, Y. G., Kim, J., Jung, Y., Cho, H.-K., Kim, J., and Koo, J.-H.*: Cloud impacts on Korea shortwave radiation budget: estimation from a deterministic model with surface measurements, Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-020-00196-0
- Kim, J., Lee, Y. G.*, Koo, J.-H., and Lee, H.: Relative contributions of clouds and aerosols to surface erythemal UV and global horizontal irradiance in Korea, Energies, 13, 1504, 2020; doi:10.3390/en13061504.
2019
- Ahn, D. H., Choi, T., Kim, J., Park, S. S., Lee, Y. G., Kim, S.-J., and Koo, J.-H.: Southern Hemisphere mid- and high-latitudinal AOD, CO, NO2, and HCHO: spatiotemporal patterns revealed by satellite observations, Progress in Earth and Planetary Science, 6(34), 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40645-019-0277-y
- Park, S. S., Cho, H.-K., Koo, J.-H., Lim, H. K., Lee, H., Kim, J., and Lee, Y. G.*: Monitoring and long-term trend of total column ozone from Dobson spectrophotometer in Seoul (1985~2017), Atmosphere , 29, 13-20, 2019. (Korea domestic)
- Lee, H., Kim, W., Lee, Y. G., Koo, J.-H., Jung, Y., Park, S., Cho, H. -K., Kim, J.: Broadband dependence of atmospheric transmissions in the UV and total solar radiation, Tellus B: Chemical & Physical Meteorology, 71(1), 1-12, 2019.
- Park, S., Lee, Y. G.*, Kim, M., Kim, J., Koo, J.-H., Kim, C. K., Um, J., and Yoon, J.: Simulation of threshold UV exposure time for vitamin D synthesis in South Korea, Advances in Meteorology, Volume 2019, Article ID 4328151, 15 pages, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4328151.
2018
- Ahn, D. H., Choi, T., Kim, J., Park, S. S., Lee, Y. G., Kim, S.-J., and Koo, J.-H.: Southern Hemisphere mid- and high-latitudinal AOD, CO, NO2, and HCHO: spatiotemporal patterns revealed by satellite observations, Progress in Earth and Planetary Science, 6(34), 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40645-019-0277-y
- Park, S. S., Cho, H.-K., Koo, J.-H., Lim, H. K., Lee, H., Kim, J., and Lee, Y. G.*: Monitoring and long-term trend of total column ozone from Dobson spectrophotometer in Seoul (1985~2017), Atmosphere , 29, 13-20, 2019. (Korea domestic)
- Lee, H., Kim, W., Lee, Y. G., Koo, J.-H., Jung, Y., Park, S., Cho, H. -K., Kim, J.: Broadband dependence of atmospheric transmissions in the UV and total solar radiation, Tellus B: Chemical & Physical Meteorology, 71(1), 1-12, 2019.
- Park, S., Lee, Y. G.*, Kim, M., Kim, J., Koo, J.-H., Kim, C. K., Um, J., and Yoon, J.: Simulation of threshold UV exposure time for vitamin D synthesis in South Korea, Advances in Meteorology, Volume 2019, Article ID 4328151, 15 pages, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4328151.
2017
- Kim, J., Kim, J., Cho, H. -K., Herman, J., Park, S., Lim, H. K., Kim, J. -H., Miyagawa, K., and Lee, Y. G.: Intercomparison of total column ozone data from the Pandora spectrophotometer with Dobson, Brewer, and OMI measurements over Seoul, Korea, Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 10, 3661-3671, 2017.
- Park, S., Kim, M., Lee, H., Lee, H., Kim, S. M., and Lee, Y. G.*: Estimating cloud and aerosol UV modification factors based on spectral measurement from the Brewer Spectrophotometer, Atmosphere, 8, 109, 2017.
- Kim, D., Lee, H.*, Hong, H., Choi, W., Lee, Y. G., and Park, J.: Estimation of surface NO2 volume mixing ratio in four metropolitan cities in Korea using multiple regression models with OMI and AIRS data, Remote Sensing, 9, 627, 2017.
- Mok, J., Park, S. S., Lim, H., Kim, J., Lee, Y. G., Lee, J., Edwards, D. P., Yoon, J., Koo, J.-H.*: Correlation analysis between regional carbon monoxide and black carbon from satellite measurements, Atmospheric Research, 196, 29-39, 2017.
- Jeong, U., Kim, J.*, Lee, H., and Lee, Y. G.: Assessing the effect of long-range pollutant transportation on air quality in Seoul using the conditional potential source contribution function method, Atmospheric Environment, 150, 33-44, 2017.
2016
- Koo, J.-H., Kim, J., Kim, J., Lee, H., Noh, Y. M., and Lee, Y. G.*: Springtime trans-Pacific transport of Asian pollutants characterized by the Western Pacific (WP) pattern, Atmospheric Environment, 147, 166-177, 2016.
- Koo, J.-H., Kim, J.*, Lee, J., Eck, T. F., Lee, Y. G., Park, S., Kim, M., Jeong, U., Yoon, J., Mok, J., and Cho, H. -K.: Wavelength dependence of Angstrom exponent and single scattering albedo observed in Seoul, Korea, Atmospheric Research, 181, 12-19, 2016.
- Park, S., Jung, Y., and Lee, Y. G.*: Spectral dependence on the correction factor of erythemal UV for cloud, aerosol, total ozone, and surface properties: A modeling study, Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 33, 865-874, 2016.
- Jung, Y., Lee, H., Kim, J., Cho, Y., Kim, J., and Lee, Y. G.*: Spatio-temporal characteristics in the clearness index derived from global solar radiation observations in Korea, Atmosphere, 7, 55, 2016.
- Yoon, J.*, Pozzer, A., Chang, D. Y., Lelieveld, J., Kim, J., Kim, M., Lee, Y. G., Koo, J.-H., Lee, J., and Moon, K. J.: Trend estimates of AERONET-observed and model-simulated AOTs between 1993 and 2013, Atmospheric Environment, 125, 33-47, 2016.
2015
- Park, S., Lee, Y. G.*, and Kim, J. H.: Impact of UV-A radiation on erythemal UV and UV-index estimation over Korea, Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 32, 1639-1646, 2015.
- Lee, Y. G., Ho, C.-H.*, Kim, J.-H., and Kim, J.: Quiescence of Asian dust events in South Korea and Japan during 2012 spring: Dust outbreaks and transports, Atmospheric Environment, 114, 92-101, 2015.
- Lee, Y. G., Koo, J.-H.*, and Kim, J.: Influence of cloud fraction and snow cover to the variation of surface UV radiation at King Sejong station, Antarctica, Atmospheric Research, 164-165, 99-109, 2015.
- Jung, C.* H., Um J., Shin, Y. H., Lee, S. S., Lee, Y. G., Bae, S. Y., and Kim, Y. P.: Minimum collection efficiency diameter during snow scavenging process, Particulate Science and Technology, 33, 321-330, 2015.
2014
- Hong, H., Lee, H.*, Kim, J., and Lee, Y. G.,: First comparison of OMI-DOAS total ozone using ground-based observations at a megacity site in East Asia: Causes of discrepancy and improvement in OMI-DOAS total ozone during summer, Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 119, 10,058-10,067, 2014.
- Lee, Y. G., Kim, J.*, Ho, C.-H., An, S.-I., Cho, H.-K., Mao, R., Tian, B., Wu, D., Lee, J. N., Kalashnikova, O., Choi, Y., and Yeh, S.-W.: The effects of ENSO under negative AO phase on spring dust activity over northern China: an observational investigation, International Journal of Climatology, 35, 935-947, 2014.
- Lee, J., Kim, J.*, and Lee, Y. G.: Simultaneous retrieval of aerosol properties and clear-sky direct radiative effect over the global ocean from MODIS, Atmospheric Environment, 92, 309-317, 2014.
2013
- Lee, S., Ho, C.-H.*, Lee, Y. G., Choi, H.-J., and Song, C.-K.: Influence of transboundary air pollutants form China on the high-PM10 episode in Seoul, Korea for the period October 16-20, 2008, Atmospheric Environment, 77, 430-439, 2013.
- Lee, Y. G., Ho, C.-H.*, Kim, J., Kim, J.: Potential impacts of northeastern Eurasian snow cover on generation of dust storms in northwestern China during spring, Climate Dynamics, 41, 721-733, 2013.
2012
- Park, S., Kim, J.*, Cho, N., Lee, Y. G., and Cho, H.-K.: The variations of stratospheric ozone over the Korean Peninsula 1985~2009, Atmosphere, 21(4), 349-359, 2011. (Korea domestic)
- Lee, Y. G., Kim, J.*, Cho, H.-K., Song, C. H.: Regional forecast of the UV index with optimized total ozone prediction using satellite observations over East Asia, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 30, 22, 6035-6051, 2009.
- Cho, H.-K., Kim, J.*, Jung, Y., and Lee, Y. G.: Recent changes in downward long wave radiation at King Sejong station, Antarctica, Journal of Climate, 21, 5764-5776, 2008.
- Lee, Y. G., Kim, J.*, Cho, H.-K., Choi, B. C., Kim, J., Chung, S. R., and Park, I. S.: Forecast of UV-index over Korea with improved total ozone prediction and effects of aerosols, clouds, and surface albedo, Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 44, 4, 381-400, 2008.
- Kim, J.*, Park, S., Moon, K. J., Koo, J.-H., Lee, Y. G., Miyagawa, K., and Cho, H.-K.: Automation of Dobson spectrophotometer (NO. 124) for ozone measurements, Atmosphere, 17(4), 339-348, 2007. (Korea domestic)



